Employment Application Apply
What is a Thin Layer Evaporator and How Does It Work
In the realm of thermal separation technologies, a thin layer evaporator stands out as a pivotal component in processes aimed at efficiently concentrating liquids. According to a 2021 market research report by Global Industry Analysts, the global thin layer evaporator market is projected to reach USD 400 million by 2027, propelled by the growing demand for food processing and chemical production. This technology facilitates enhanced heat transfer and reduced thermal degradation of sensitive products, making it a preferred choice in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and biofuels.
Dr. Emily Turner, a leading expert in thermal separation technologies, emphasizes the significance of thin layer evaporators by stating, “The ability of thin layer evaporators to minimize energy consumption while maximizing product yield is transforming how industries approach liquid concentration.” With their innovative design that allows for a faster evaporation rate and lower boiling point, these evaporators are increasingly recognized for their efficiency.
As industries strive for sustainable practices, the role of thin layer evaporators in energy conservation and resource optimization will only grow in importance, representing a critical innovation in modern manufacturing processes.

Definition of a Thin Layer Evaporator and Its Purpose
A thin layer evaporator is an essential piece of equipment commonly utilized in various industries, particularly in chemical processing, food production, and pharmaceuticals. It operates on the principle of separating solvents from solutes through evaporation. The primary purpose of a thin layer evaporator is to concentrate solutions efficiently, allowing for the effective removal of volatile components while preserving the integrity of the product. This technology is especially advantageous in processes requiring gentle handling of heat-sensitive materials.
In practice, a thin layer evaporator coats the feed material in a thin film across a heated surface. As the feed is thermally treated, the solvent evaporates, leaving behind the concentrated solutes. The design of the evaporator facilitates a high surface area to volume ratio, ensuring maximum heat transfer and minimizing the risk of thermal degradation. By maintaining a thin film, the evaporator can operate at lower pressures and temperatures compared to traditional evaporators, thus enhancing energy efficiency and product quality. This makes thin layer evaporators particularly valuable for applications where maintaining the flavor, aroma, or biochemical properties of the original material is crucial.
Key Components of a Thin Layer Evaporator System
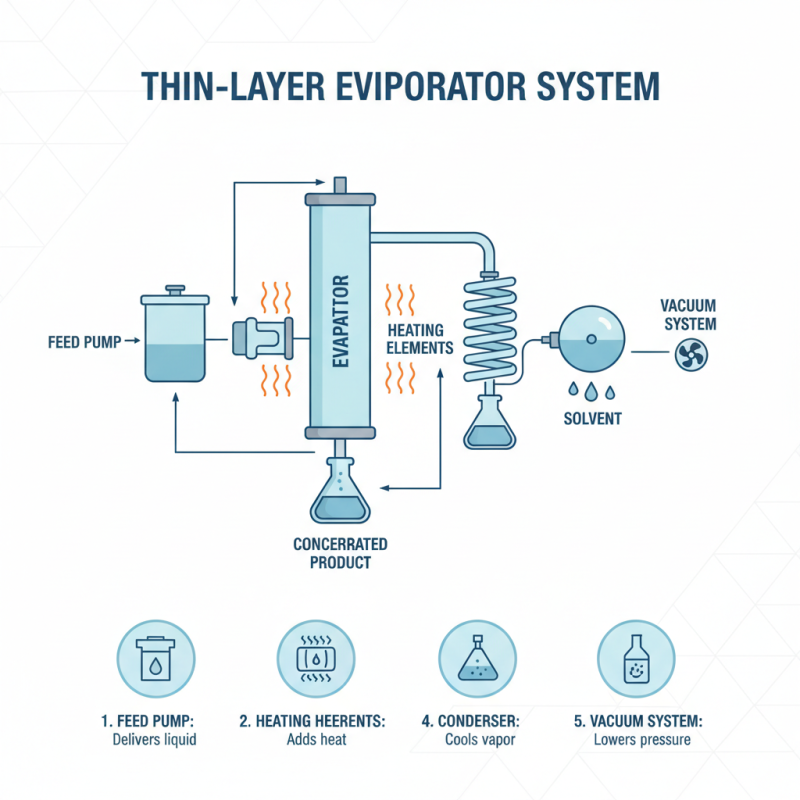
A thin layer evaporator is a specialized device commonly used in various industrial processes to efficiently remove solvents from liquid mixtures. The key components of a thin layer evaporator system include the evaporator itself, a feed pump, heating elements, a condenser, and a vacuum system. Each component plays an essential role in optimizing the evaporation process.
The evaporator is designed to create a thin film of liquid on a heated surface, which promotes rapid evaporation. The feed pump ensures a consistent flow of the liquid mixture onto the evaporator's surface, while the heating elements raise the temperature to facilitate solvent removal. Meanwhile, the condenser captures the vapor produced during the evaporation process, allowing for product recovery. Additionally, a vacuum system can be integrated to lower the boiling point of the solvent, enhancing efficiency.
**Tips:** When selecting a thin layer evaporator, consider the nature of the liquid being processed, as this can significantly affect the efficiency of evaporation. Regular maintenance of the components, particularly the condenser and pump, is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prolong the lifespan of the system. Always refer to operational guidelines to adjust parameters for specific applications.
Principle of Operation: How a Thin Layer Evaporator Functions
A thin layer evaporator is an efficient device used in industrial processes to separate volatile solvents from non-volatile components. The principle of operation behind a thin layer evaporator is relatively straightforward yet highly effective. The material to be processed is spread into an extremely thin layer on a heated surface. This configuration allows for a large surface area contact between the liquid and the heating surface, facilitating rapid evaporation of the solvent.
As the heat is applied, the thin layer of liquid rapidly warms up, causing the more volatile components to vaporize quickly. The vapors are then collected and condensed for further use, while the residual non-volatile portion remains on the surface. This method not only enhances evaporation rates but also minimizes thermal degradation of sensitive substances, which is crucial in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
Tip: To optimize the performance of a thin layer evaporator, regularly check and maintain the heating element and ensure proper adjustments to the feed rate. This will help prevent issues such as fouling and improve overall efficiency. Monitoring the temperature can also help maintain optimal conditions for evaporation, ensuring high-quality outputs.
Applications of Thin Layer Evaporators in Various Industries
Thin layer evaporators are widely utilized across various industries due to their efficiency in concentrating and purifying liquid products. In the food and beverage industry, these evaporators play a crucial role in concentrating juices, sauces, and dairy products while preserving the flavor and nutritional quality. By operating at lower temperatures, thin layer evaporators minimize thermal degradation, making them ideal for sensitive materials that require gentle processing.
In the pharmaceutical and chemical sectors, thin layer evaporators are instrumental in separating solvents from mixtures and concentrating active ingredients. Their design allows for rapid evaporation, reducing processing time significantly. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in producing high-purity compounds where stringent quality control is necessary.
Furthermore, industries involved in bioprocessing use thin layer evaporators to concentrate culture media and extract valuable metabolites, thus optimizing production processes and resource utilization. Overall, their versatility and effectiveness render thin layer evaporators an essential component in modern industrial applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Thin Layer Evaporators
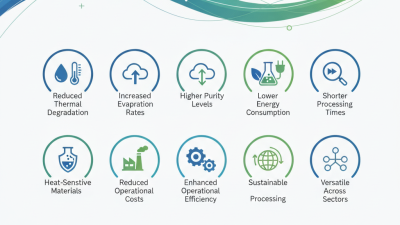
Thin layer evaporators are widely used in various industries for their efficiency in concentrating liquids, especially in processes where thermal sensitivity of the product is a concern. One of the primary advantages of thin layer evaporators is their ability to operate at lower temperatures and reduce the risk of thermal degradation. According to a report by the International Journal of Chemical Engineering, thin layer evaporators can achieve evaporation rates that are 30% higher than traditional evaporators, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
However, there are also disadvantages associated with the use of thin layer evaporators. One significant drawback is the initial capital investment, which can be notably higher compared to other evaporator types. A market analysis from Grand View Research indicates that while the demand for thin layer evaporators is anticipated to grow, the upfront costs can be a barrier for some manufacturing facilities. Furthermore, the complexity of the systems may require specialized maintenance knowledge, adding to operational costs in the long term.
In summary, while thin layer evaporators offer notable advantages in terms of efficiency and product quality, their higher costs and maintenance requirements should be carefully considered by businesses looking to implement these systems in their manufacturing processes.
What is a Thin Layer Evaporator and How Does It Work - Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Thin Layer Evaporators
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A thin layer evaporator is a device used to concentrate liquids by evaporating solvent through a thin film. |
| Working Principle | Material is spread in a thin film over a heated surface to facilitate rapid evaporation. |
| Advantages | High efficiency, low energy consumption, gentle treatment of heat-sensitive materials. |
| Disadvantages | Higher initial investment costs, potential for corrosion, requires continuous operation for best results. |
| Applications | Used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries for concentrating liquids. |
| Common Materials Processed | Sugars, fruit purees, essential oils, and chemical solutions. |