Employment Application Apply
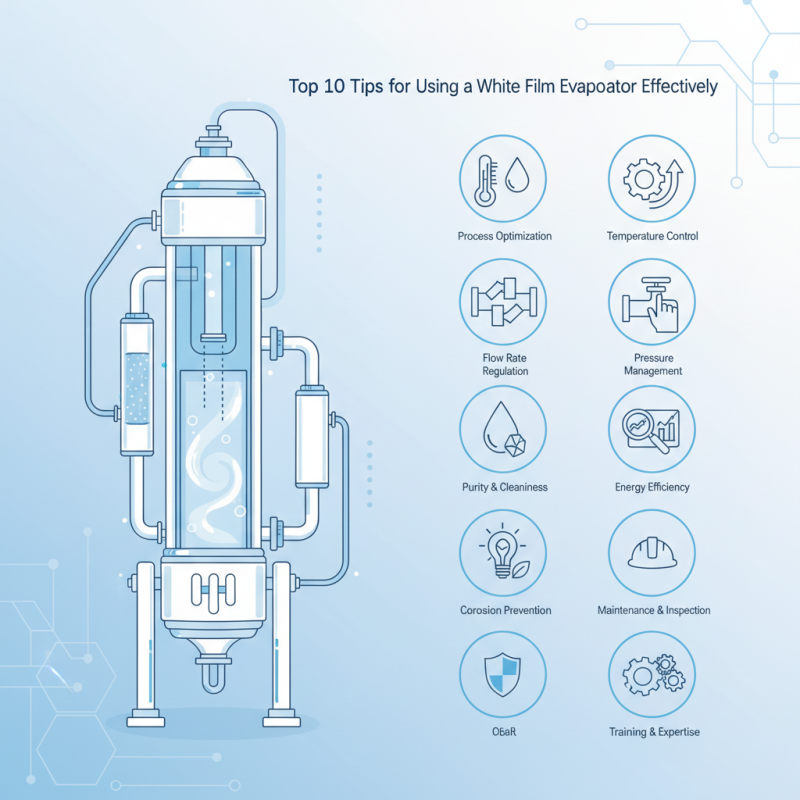
Top 10 Tips for Using a White Film Evaporator Effectively
In the realm of thermal separation technologies, the white film evaporator stands out as a pivotal piece of equipment for efficient mass and heat transfer. Renowned expert Dr. James Hawthorne, a leading voice in the field of chemical engineering, emphasizes the significance of this technology by stating, "The white film evaporator not only enhances the efficiency of concentration processes but also improves product quality through its unique thermal characteristics." As industries strive for efficiency and sustainability, mastering the use of the white film evaporator becomes crucial.
Achieving optimal performance with a white film evaporator requires an understanding of its operational dynamics and best practices. Whether you are involved in food processing, pharmaceuticals, or chemical production, employing effective techniques can significantly impact your process outcomes. This article presents the top 10 tips for using a white film evaporator effectively, ensuring that both seasoned professionals and newcomers can navigate the complexities of this essential technology with confidence and precision. With these strategies, users can maximize efficiency, lower energy consumption, and ultimately enhance their product quality.
Understanding the Basics of White Film Evaporators
White film evaporators are essential tools in various industrial processes, notably in the food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries. The technology utilizes a thin film of liquid that is rapidly evaporated to achieve concentration, separation, or purification of substances. According to a recent market analysis report from a leading industry research firm, the global market for evaporators is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.7% from 2023 to 2030, indicating a rising demand for efficient evaporation techniques across multiple sectors.
In the context of operating white film evaporators effectively, understanding their basic principles is crucial. The efficiency of these systems largely depends on factors such as film thickness, temperature differential, and the properties of the substance being processed. Research indicates that optimal operation typically occurs when maintaining a thin film of 0.5 to 1 mm; this ensures minimal thermal degradation and maximizes the evaporation surface area. Furthermore, maintaining an appropriate temperature can significantly reduce processing time while improving product quality; studies have shown that operating within a specific temperature range can lead to energy savings of up to 30%, underlining the economic benefit of well-managed evaporation operations.
In conclusion, comprehending the fundamental mechanics of white film evaporators not only enhances their operational efficiency but also contributes to superior product outputs. Continuing advancements in this area promise to further expand their utility across various industries, underscoring the need for ongoing education and adaptation to best practices in evaporation technology.
Top 10 Tips for Using a White Film Evaporator Effectively
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maintain proper temperature settings | Improved efficiency and product quality |
| 2 | Regularly clean and maintain equipment | Reduced downtime and maintenance costs |
| 3 | Optimize feed flow rates | Maximized evaporation performance |
| 4 | Monitor process parameters continuously | Consistent output and quality assurance |
| 5 | Use suitable heating media | Enhanced heat transfer efficiency |
| 6 | Implement effective vacuum control | Improved separation of components |
| 7 | Perform regular performance assessments | Identify areas for improvement |
| 8 | Train operators on system operations | Increased safety and efficiency |
| 9 | Ensure proper insulation of evaporator | Reduced energy consumption |
| 10 | Analyze and adjust operational parameters | Optimal performance and output |
Key Factors Influencing Evaporation Efficiency
When it comes to maximizing the efficiency of white film evaporators, several key factors play a pivotal role in influencing evaporation efficiency. One of the most significant factors is the film thickness on the heat transfer surface. Studies indicate that thinner films generally lead to better heat transfer rates. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, reducing the film thickness can enhance the evaporation rate by approximately 30% under optimized conditions. This is largely due to improved heat conduction and reduced thermal resistance, ultimately leading to increased productivity.
Another critical factor is the temperature differential between the heating medium and the evaporating solution. Research published in the Journal of Food Engineering highlights that an optimal temperature difference can significantly enhance the evaporation rate. It was found that maintaining a temperature gradient of 20°C to 30°C across the evaporator can improve the overall thermal efficiency by as much as 25%. Furthermore, the selection of the heating medium, whether steam or thermal oil, also impacts the heat transfer efficiency, with steam usually offering superior performance due to its high latent heat of vaporization.
Finally, the design of the evaporator plays a vital role in determining the efficiency of the process. Factors such as the configuration of the heat exchanger, the flow patterns of the liquid and vapor phases, and the choice of materials can have substantial effects on heat transfer rates. According to a technical report from the International Institute of Refrigeration, optimizing these design parameters can lead to improvements in energy efficiency of up to 50%. By focusing on these critical aspects, operators can significantly enhance the performance of white film evaporators, leading to reduced operational costs and improved output.
Best Practices for Pre-treatment of Feed Solutions
When preparing feed solutions for a white film evaporator, the pre-treatment stage is crucial in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. One of the key practices is to ensure that the feed solution is free from large particulates and impurities. This can be achieved by employing filtration systems or sedimentation techniques, which help to prolong the lifespan of the evaporator and prevent potential blockages during operation. Maintaining an appropriate particulate size distribution also helps enhance heat transfer efficiency during the evaporation process.
Another significant aspect of pre-treatment involves adjusting the temperature and pH of the feed solution. Preheating the feed can reduce the viscosity of viscous solutions, making it easier for the evaporator to work efficiently. Moreover, maintaining the optimal pH level can improve the stability of the solution, ultimately minimizing the risk of fouling and scaling within the evaporator. Monitoring these parameters prior to the evaporation process ensures that the system operates at peak performance, allowing for consistent product quality and reduced operational downtime.
Top 10 Tips for Using a White Film Evaporator Effectively
This bar chart illustrates the importance of various tips for effectively using a white film evaporator in the pre-treatment of feed solutions. The data represents the effectiveness rating (on a scale of 1 to 10) based on expert recommendations.
Monitoring and Adjusting Operational Parameters
In the operation of a white film evaporator, monitoring and adjusting the operational parameters are crucial for maintaining efficiency and product quality. One of the primary aspects to monitor is the feed rate. A consistent feed rate ensures that the evaporation process remains stable, allowing for optimal heat transfer and minimizing fluctuations that could lead to poor product quality or increased energy consumption. Regularly checking the feed rate allows operators to make necessary adjustments based on the desired concentration of the solution being processed.
Another important operational parameter is the temperature profile within the evaporator. Maintaining the appropriate temperature is essential to achieving the desired evaporation rate without decomposing sensitive materials. Operators should utilize temperature sensors and control systems to continuously monitor and adjust the vapor and liquid temperatures. By being vigilant about these readings, operators can promptly respond to any deviations, ensuring that the process runs smoothly and that the final product meets specifications. Ultimately, careful monitoring and adjustment of these parameters facilitate enhanced control over the evaporation process, leading to improvements in efficiency and product integrity.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Techniques

When operating a white film evaporator, users may encounter several common challenges that can hinder the efficiency of the process. One frequent issue is the formation of fouling on the heat transfer surfaces. This can result from inadequate cleaning or the buildup of materials that negatively affect heat transfer rates. To address this, regular maintenance and routine cleaning schedules are essential. Users should monitor the performance of the evaporator closely and employ techniques such as chemical cleaning or mechanical brushing to maintain optimal conditions.
Another challenge is controlling the evaporation rate, which can lead to either dry or wet distillate issues. Inconsistent temperatures and flow rates can cause fluctuations that impact product quality. To troubleshoot this, operators should ensure that the heat source is stable and that the feed rate is appropriately adjusted according to the desired concentration. Implementing automated controls can significantly improve the precision of these parameters, reducing the risk of operational disturbances and ensuring a consistent output that meets quality standards.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Benefits of Thin Film Evaporators for Efficient Distillation Processes
-

What is a Thin Layer Evaporator and How Does It Work
-

Top 5 Tips for Using LCI Wiped Film Evaporators Effectively
-
2025 Top Film Evaporator Technologies and Trends You Need to Know
-

What is a VTA Thin Film Evaporator and How Does It Work
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Luwa Evaporator for Your Industrial Processes
