Employment Application Apply
How to Understand the Working Principle of Falling Film Evaporator?
The working principle of falling film evaporator is a key aspect of its functionality. This device is widely used in various industries for efficient heat transfer and separation processes. Understanding how it operates can enhance its application in diverse scenarios.
In a falling film evaporator, a thin film of liquid flows down a vertical surface. This film is created by introducing the feed solution at the top. As gravity acts on the liquid, it films down, allowing for rapid evaporation. The design promotes a large surface area, boosting heat transfer efficiency.
However, the working principle of falling film evaporator has its challenges. For instance, maintaining an even film thickness can be difficult. Uneven distribution may lead to decreased efficiency and increased energy consumption. These factors need careful consideration during operation. Understanding these details is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring effective use.
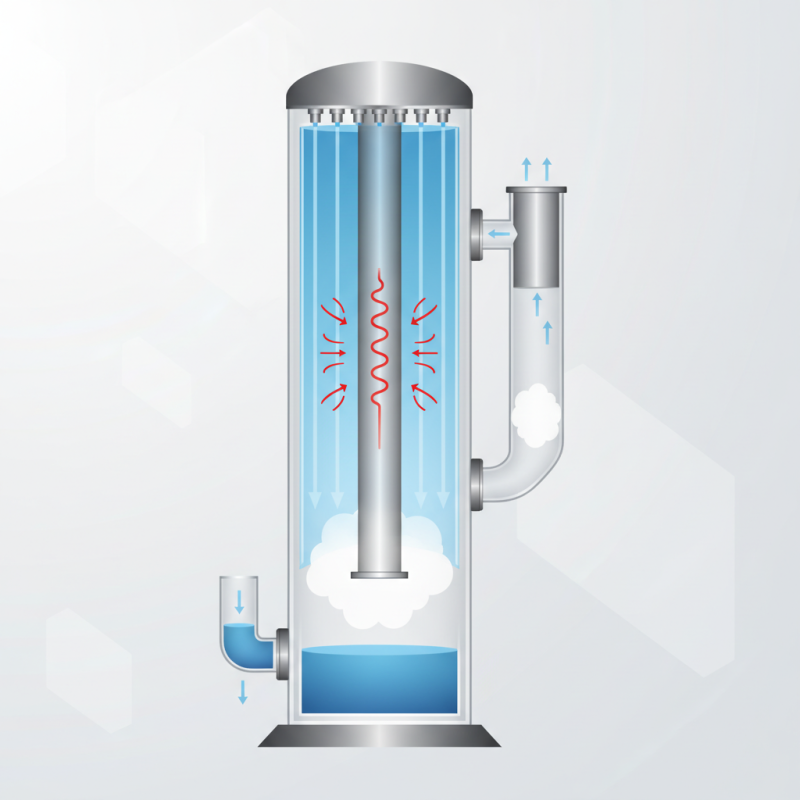
Understanding the Concept of Falling Film Evaporators in Industry
Falling film evaporators play a crucial role in many industries. They are commonly used for concentrating liquid solutions. The method involves the liquid forming a thin film on a heated surface. This approach allows for efficient heat transfer and rapid evaporation. According to industry reports, the global market for falling film evaporators is projected to reach USD 4 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 5.2%.
These evaporators are essential for processes like sugar, dairy, and chemical production. Their design allows for low-temperature evaporation. This characteristic helps preserve sensitive components in food and pharmaceuticals. However, operating falling film evaporators can present challenges. Maintaining optimal flow rates is vital. If the film becomes too thick, it can lead to inefficiencies and fouling. Industry reports indicate that improper operation may account for up to 30% of energy wastage in some facilities.
Moreover, maintenance keeps these units running efficiently. Regular checks are necessary to prevent scaling and corrosion. Despite the technical advances, some systems still struggle with troubleshooting. Many operators need better training on the nuances of these systems. For an industry reliant on precision, these gaps can lead to costly errors. Addressing these issues is essential for maximizing performance and reducing costs.
How to Understand the Working Principle of Falling Film Evaporator?
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Concentration | 10 | % w/w |
| Evaporator Area | 50 | m² |
| Operating Temperature | 80 | °C |
| Evaporation Rate | 5 | kg/h |
| Reboiler Duty | 25 | kW |
| Number of Stages | 1 | |
| Liquid Film Thickness | 0.5 | mm |
Key Components and Design Features of Falling Film Evaporators
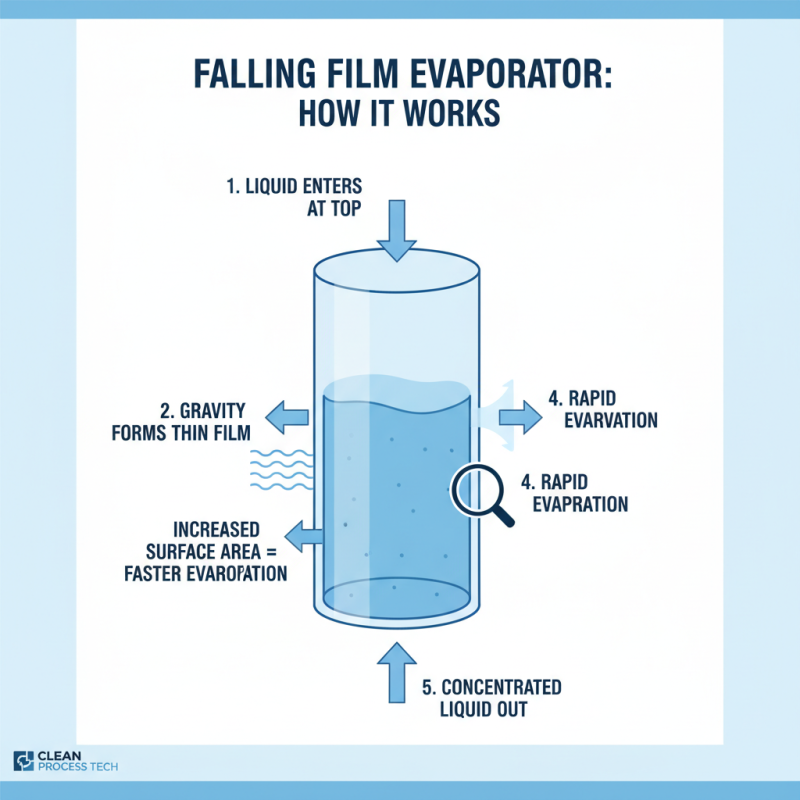
Falling film evaporators operate on a simple yet effective principle. They utilize gravity to form a thin film of liquid over a heated surface. This design enhances heat transfer efficiency, allowing for rapid evaporation. The liquid enters at the top and flows downwards, creating a uniform thin layer. As the film descends, its surface area increases, promoting faster evaporation.
Key components include the evaporation chamber, feed distributors, and heating elements. The evaporation chamber is where the main action occurs. Inside, the feed distributors ensure an even flow of liquid. This prevents uneven film thickness, which can lead to inefficiencies. Heating elements maintain consistent temperature throughout the process.
Design features also play a crucial role. Counterflow and parallel flow arrangements can impact the overall performance. However, achieving the right balance can be challenging. A common issue is optimizing the film thickness for various fluid properties. Too thick can slow evaporation, while too thin might affect heat transfer. Understanding these nuances is vital for effective evaporator operation.
The Thermal and Fluid Dynamics in Falling Film Evaporation Process
Falling film evaporators operate on unique thermal and fluid dynamics principles. In this process, a thin film of liquid flows down a vertical surface. This design enhances heat transfer rates, enabling efficient evaporation. According to the International Journal of Chemical Engineering, the heat transfer coefficient can reach up to 3000 W/m²·K in optimized systems. Such efficiency is crucial for industries seeking reduced energy costs.
The liquid's behavior is influenced by various factors, including flow rates and temperature differentials. Studies indicate that film thickness significantly impacts performance. A thinner film generally results in better heat transfer but may require tighter controls. Achieving the optimal balance can be challenging. Each adjustment affects overall thermal efficiency and can lead to complications.
Fluid dynamics play a pivotal role in the evaporation process. Flow patterns can change based on temperature and pressure settings. At times, unpredictable behaviors may arise, where liquid can break up into droplets. This phenomenon results in less efficient evaporation and invites additional considerations for operators. The goal remains clear: maximize efficiency while managing these complex interactions.
Efficiency Metrics: Evaluating the Performance of Falling Film Evaporators

Falling film evaporators are noteworthy for their efficiency in heat transfer. Their performance can be evaluated using specific metrics. Understanding these metrics helps in optimizing processes in various industries. Key efficiency factors include thermal efficiency, energy consumption, and overall recovery rate.
Thermal efficiency is essential. It measures how effectively the evaporator converts heat into vapor. A higher thermal efficiency often indicates better performance. Energy consumption is another critical metric. Lower energy use indicates a more efficient system. Overall recovery rate shows how much solvent is recovered after evaporation. A high recovery rate reduces waste and improves profitability.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance can enhance efficiency. Check for leaks and inspect the heating surfaces regularly. This maintains performance and prevents costly downtimes.
Monitoring these metrics helps identify potential improvements. Small changes can have significant impacts on overall performance. Continual evaluation is essential for long-term success. Don't overlook the importance of proper training for operators. Knowledgeable staff contribute to better management of the equipment and processes.
Applications and Benefits of Falling Film Evaporators in Different Sectors
Falling film evaporators play a crucial role in various industries. They are used for concentrating liquids, especially in food and beverage sectors. These systems utilize a thin film of liquid to increase evaporation efficiency. This allows for better heat transfer and reduced energy consumption. Other applications include chemical processing and pharmaceuticals.
The benefits are significant. Falling film evaporators can handle heat-sensitive products. This is vital in preserving flavor and nutrients in food processing. Moreover, they require less space compared to traditional evaporators. Their compact design is ideal for facilities with limited space.
**Tip:** Always consider the product's thermal properties before selecting an evaporator. Understanding these properties can improve the efficiency of the process.
In certain cases, challenges may arise. Foaming can occur during operation, affecting performance. Regular monitoring is essential to prevent such issues. Adjusting the operating conditions may help in managing these challenges. This adaptability can lead to increased productivity in the long term.
Applications of Falling Film Evaporators in Various Industries
This bar chart illustrates the various applications of falling film evaporators across different sectors, highlighting their benefits and usage frequency.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Luwa Evaporator for Your Industrial Processes
-

Why Choose a Luwa Thin Film Evaporator for Your Industrial Process Needs
-

What is a VTA Thin Film Evaporator and How Does It Work
-

Wiped Film Evaporator Tips for Efficient Operation and Maintenance?
-
2026 Best Pfaudler Wiped Film Evaporator Features and Benefits Explained?
-

Top 10 Benefits and Applications of Pope Wiped Film Evaporator Technology
