Employment Application Apply
What is a VTA Thin Film Evaporator and How Does It Work?
A VTA thin film evaporator is a specialized device used in various industries. It plays a crucial role in the separation and concentration processes. This equipment efficiently evaporates solvents from liquids, making it a valuable tool for chemical manufacturing.
The evaporator works by spreading the liquid film over heated surfaces. As it passes through, heat causes the solvent to evaporate. This process allows for the recovery of valuable components. However, optimizing the operation can be challenging. Variables such as temperature and pressure must be carefully controlled.
While the VTA thin film evaporator can provide high efficiency, it has some limitations. Maintenance can be complex and costly. In some cases, it might not be the best choice for all materials. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective utilization.
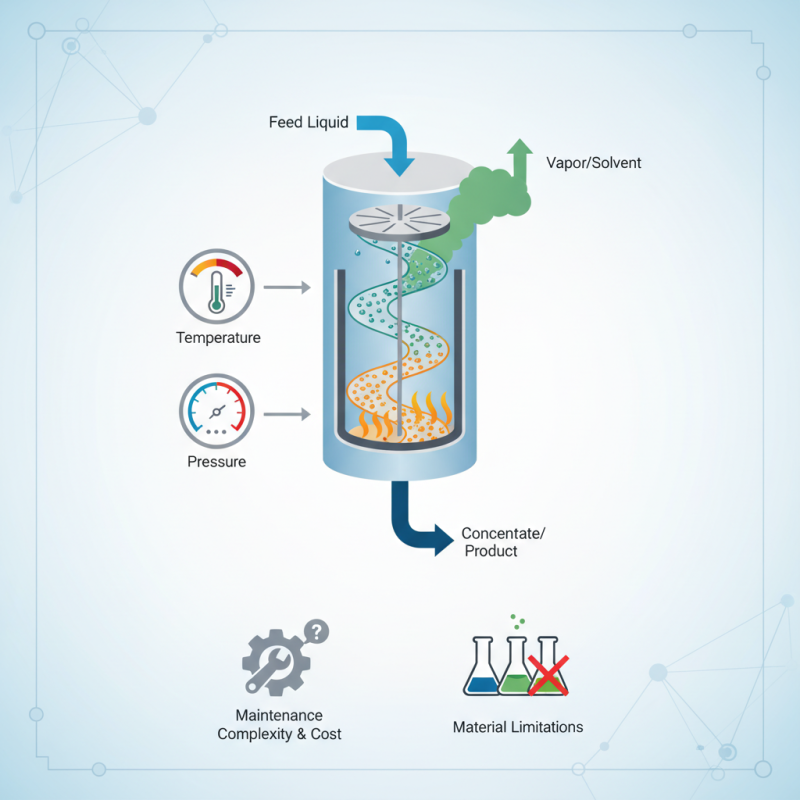
What is a VTA Thin Film Evaporator?
A VTA thin film evaporator is a crucial tool used in various industries for efficiently separating solvents from mixtures. This technology utilizes a thin film of liquid, which is spread onto a heated surface. As the film moves down, solvents evaporate rapidly. The process creates high-quality concentrated products while maintaining the integrity of heat-sensitive materials. In fact, reports indicate that thin film evaporators can achieve over over 95% solvent recovery in many applications.
When considering a VTA thin film evaporator, it’s vital to keep operational parameters in check. Factors like temperature, pressure, and film thickness can greatly influence performance. An ideal evaporator minimizes the residence time of heated materials. This reduces the risk of thermal degradation, ensuring product quality.
Tip: Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance. Check for any signs of wear and tear on components. Also, consider periodic training for operators. Understanding the equipment can prevent costly downtime or inefficient runs. It’s a mistake to underestimate the impact of skilled supervision on production efficiency.
Principles of Operation for VTA Thin Film Evaporators
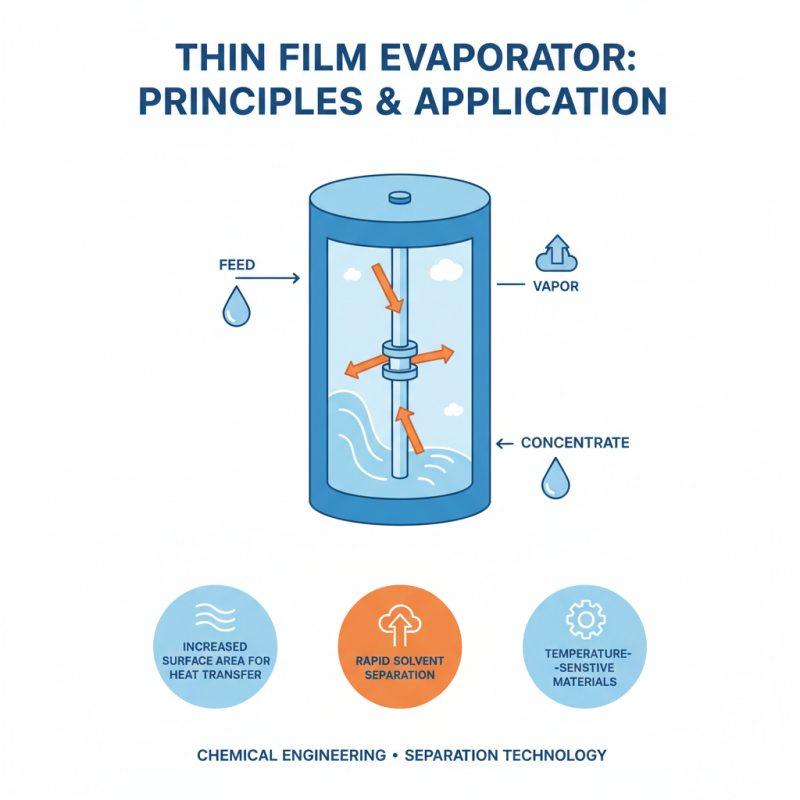
Thin film evaporators are fascinating devices in the world of chemical engineering. They operate on the principle of creating thin films of liquid material on a heated surface. This process increases the rate of evaporation, separating the components effectively. A thin liquid film enhances heat transfer. Thus, evaporation occurs rapidly in a controlled manner.
The vaporization occurs at very low residence times. As the liquid flows down the surface, it is heated. The heat causes the volatile components to evaporate. Less volatile components remain in the liquid phase. This separation is crucial for various industries, including food and pharmaceuticals.
Tips: Ensure proper heating to avoid uneven evaporation. Monitor the temperature closely. If too high, you may degrade sensitive compounds. Adjusting the feed rate is vital. Too fast, and the film may not form correctly.
Another point to consider is the material of the evaporator surface. Materials must withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. In some setups, you may encounter maintenance challenges. Regular checks can help identify wear and tear early. Addressing issues promptly can save costs and improve efficiency.
Key Components of a VTA Thin Film Evaporator
A VTA thin film evaporator is a vital piece of equipment in the chemical and food processing industries. Its design allows for efficient thermal separation of liquids. Key components of a VTA thin film evaporator include the evaporator body, heating medium, and vacuum system. The evaporator body is where the liquid feed is introduced. It has a heated surface, which promotes rapid evaporation.
Heating mediums can vary widely. Often, steam is used for its efficiency. In some reports, it is stated that optimal temperature control can enhance thermal efficiency by up to 30%. The vacuum system plays a crucial role too. By lowering the pressure, it reduces boiling points. This is particularly beneficial for heat-sensitive materials, preserving their quality.
Another significant aspect is the rotor. The rotor provides a thin film of liquid. This thin film maximizes surface area, promoting even heat distribution. Many engineers overlook the importance of regular maintenance here. Lack of upkeep can lead to uneven heating, affecting product quality. Data suggests that nearly 40% of evaporators underperform due to such issues. Addressing these elements can improve overall efficiency significantly.
Advantages of Using VTA Thin Film Evaporators
VTA thin film evaporators offer significant advantages in various industrial processes. These devices efficiently separate components from mixtures using heat. Their design allows for a larger surface area, promoting faster evaporation. This efficiency leads to shorter processing times compared to traditional evaporators.
One key benefit is the reduced thermal degradation of heat-sensitive materials. By minimizing the residence time of the liquid, it protects valuable compounds from excessive heat. This is particularly important in food and pharmaceutical industries, where quality is paramount. The continuous operation of a VTA thin film evaporator also enhances overall productivity.
However, some challenges do exist. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Operators must monitor the system closely to prevent fouling. While the technology is advanced, not every application may yield perfect results. Understanding the specific needs of the process can help maximize the benefits and address any limitations faced.
Applications of VTA Thin Film Evaporators in Industry
VTA thin film evaporators have diverse applications across various industries. They are primarily used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. In the food industry, these evaporators concentrate juices, extracts, and dairy products efficiently. By forming a thin film of liquid, heat transfer is optimized, preserving flavors and nutrients. This method often reduces processing time, leading to enhanced productivity.
In pharmaceuticals, VTA thin film evaporators play a crucial role in producing solvents and active ingredients. They enable precise concentration of solutions, necessary for drug formulation. Their ability to operate under vacuum conditions minimizes thermal degradation. However, operators must monitor parameters closely. Variations can affect product quality.
Chemical manufacturers benefit as well. VTA evaporators help recover solvents and separate compounds. However, achieving the desired separation may require adjustments. It's essential to fine-tune settings to align with process goals. Operational challenges often arise, prompting reflection on effective practices and methodologies.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Best Horizontal Thin Film Evaporator for Your Needs
-
Top 10 Benefits of Thin Film Evaporators for Efficient Distillation Processes
-

Top Benefits of Pfaudler Wiped Film Evaporators for Industrial Applications?
-
2026 Best Pfaudler Wiped Film Evaporator Features and Benefits Explained?
-
Top 10 Benefits of Luwa Thin Film Evaporator for Industrial Applications?
-

How to Optimize Your WFE Evaporator for Maximum Efficiency and Performance
